Language Meets Rehabilitation: The LUMINOUS Metacognition Chatbot Prototype
As part of the LUMINOUS project’s mission to create language-augmented XR systems that adapt intelligently to real-world complexity, we have developed a Metacognition Chatbot prototype —an AI assistant designed to support neurorehabilitation and psychoeducation through natural, context-aware conversation.
The chatbot is being integrated into the MindFocus virtual reality (VR) platform, which offers immersive cognitive rehabilitation experiences. This novel assistant helps patients and clinicians access personalized, accurate, and clinically grounded information, based on curated documents and user queries, in both English and French.
Data-Driven Intelligence: The Metacognition Chatbot Dataset
To power the chatbot’s contextual understanding, the team created a specialized Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) dataset including:
- Neurorehabilitation domain knowledge: Articles, books, infographics, and slides provided by CHUV, covering therapeutic principles and rehabilitation strategies.
- MindFocus game manual: A comprehensive 70-page guide to the MindFocus software, enabling the chatbot to explain gameplay and functionality clearly.
- Expert-designed questions: Real-world queries from clinical professionals to evaluate system responses.
This multilingual dataset ensures that the chatbot responds accurately to queries about rehabilitation practices and system use.
How It Works: Knowledge Injection in Practice
The system uses a RAG pipeline built with modern LLM components:
- Document embedding: PDF page chunks and user queries are embedded using BAAI/bgm-m3.
- Retrieval: The top-matching content is retrieved dynamically.
- Response generation: Gemini-2.0-Flash generates fluent, grounded replies based on both the query and retrieved content.
This setup ensures that the chatbot’s answers are not pre-scripted, but emerge from the model’s reasoning over relevant, domain-specific information.
Evaluation & Insights
Performance is being assessed through both manual and automated evaluation:
- Clinical experts assess responses using targeted questions.
- A RAG Triad evaluation pipeline, powered by an LLM, automatically scores:
- Context relevance
- Groundedness (i.e., how well the response is supported by retrieved data)
- Answer relevance
This multi-layered strategy enables continuous improvement, even in the absence of standard ground-truth datasets—an essential step for real-world deployments.
Strategic Alignment with LUMINOUS
The Metacognition Chatbot prototype embodies key LUMINOUS goals:
- Multilingual, multimodal intelligence: It handles complex neurorehabilitation queries in both English and French, from textual prompts to VR-integrated usage.
- Generalization beyond training data: Rather than relying solely on prior training, the chatbot dynamically incorporates new factual information using the RAG framework.
- Support for personalized interaction: By responding to the user’s context and needs, the system supports psychoeducation and informed participation in therapy.
Clinical Integration and Future Steps
The Metacognition Chatbot is being tested by neuropsychologists and speech therapists, providing valuable feedback. It is currently being embedded into pre- and post-therapy workflows in the MindFocus VR platform.
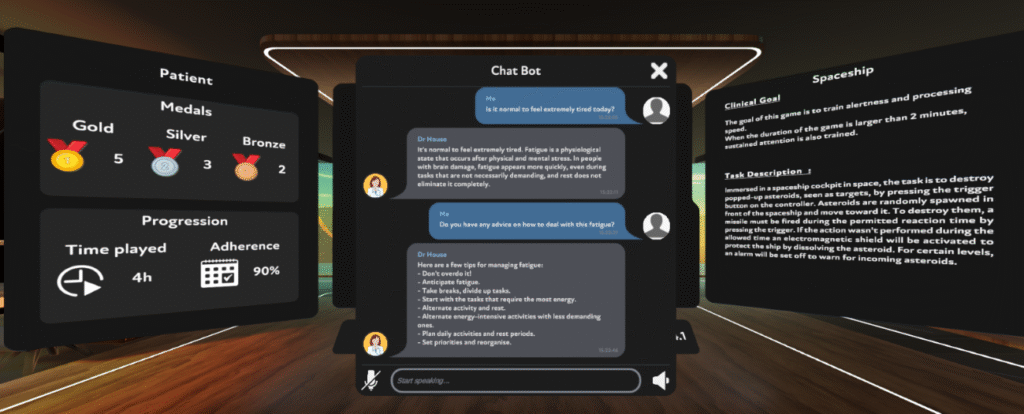
Further work includes:
- Testing with patients and real-time therapy sessions
- Expanding the evaluation dataset and refining grounding techniques
- Integrating general knowledge beyond domain-specific documents
- Developing a more “reasoned” version of the chatbot for deeper clinical interaction
A Milestone in Human-Centered XR Intelligence
By enabling conversational access to domain-specific knowledge in dynamic XR environments, the Metacognition Chatbot marks an important step toward human-centered AI for healthcare. As LUMINOUS continues to push the boundaries of what is possible at the intersection of language, cognition, and extended reality, this prototype stands as a powerful demonstration of the project’s potential.
Stay tuned for upcoming results from clinical pilots and continued development of this promising tool.
